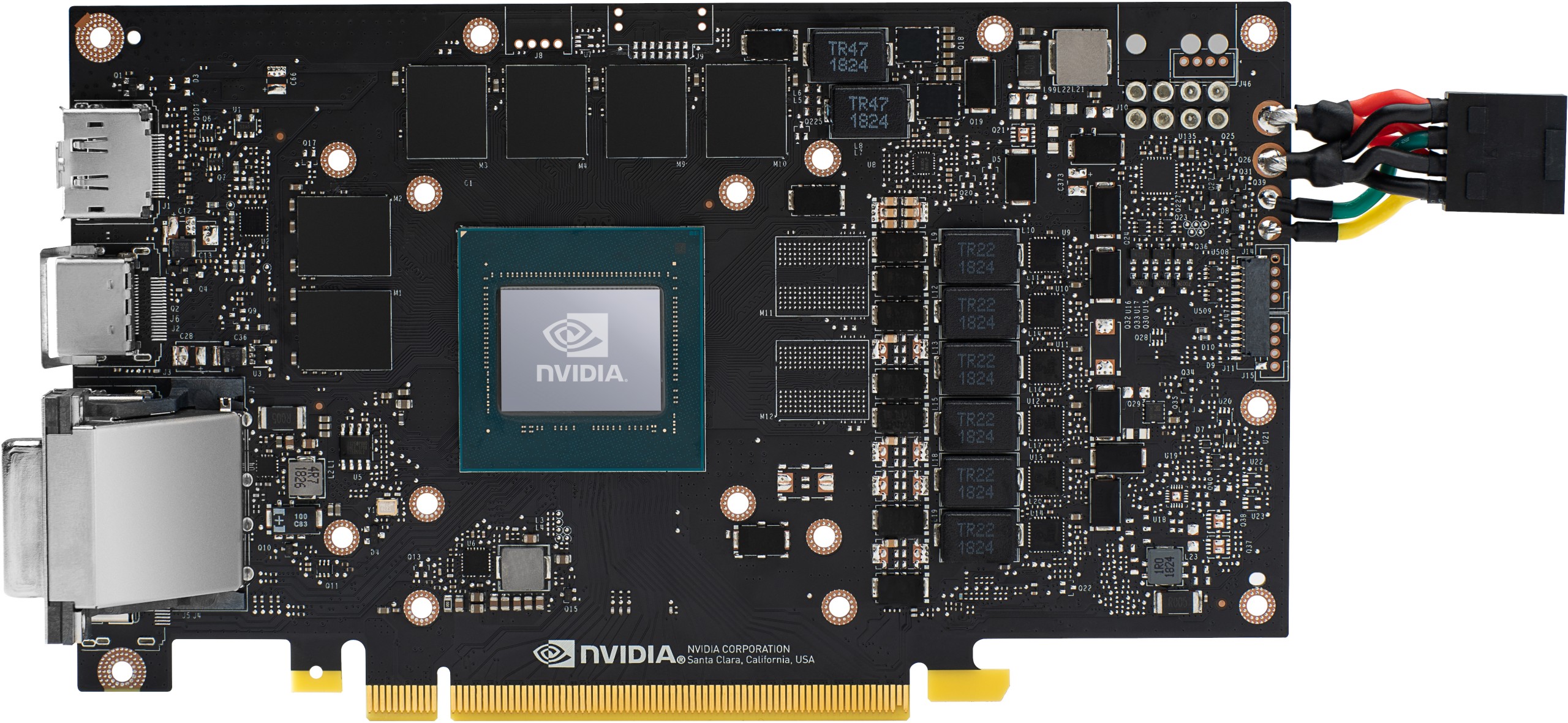
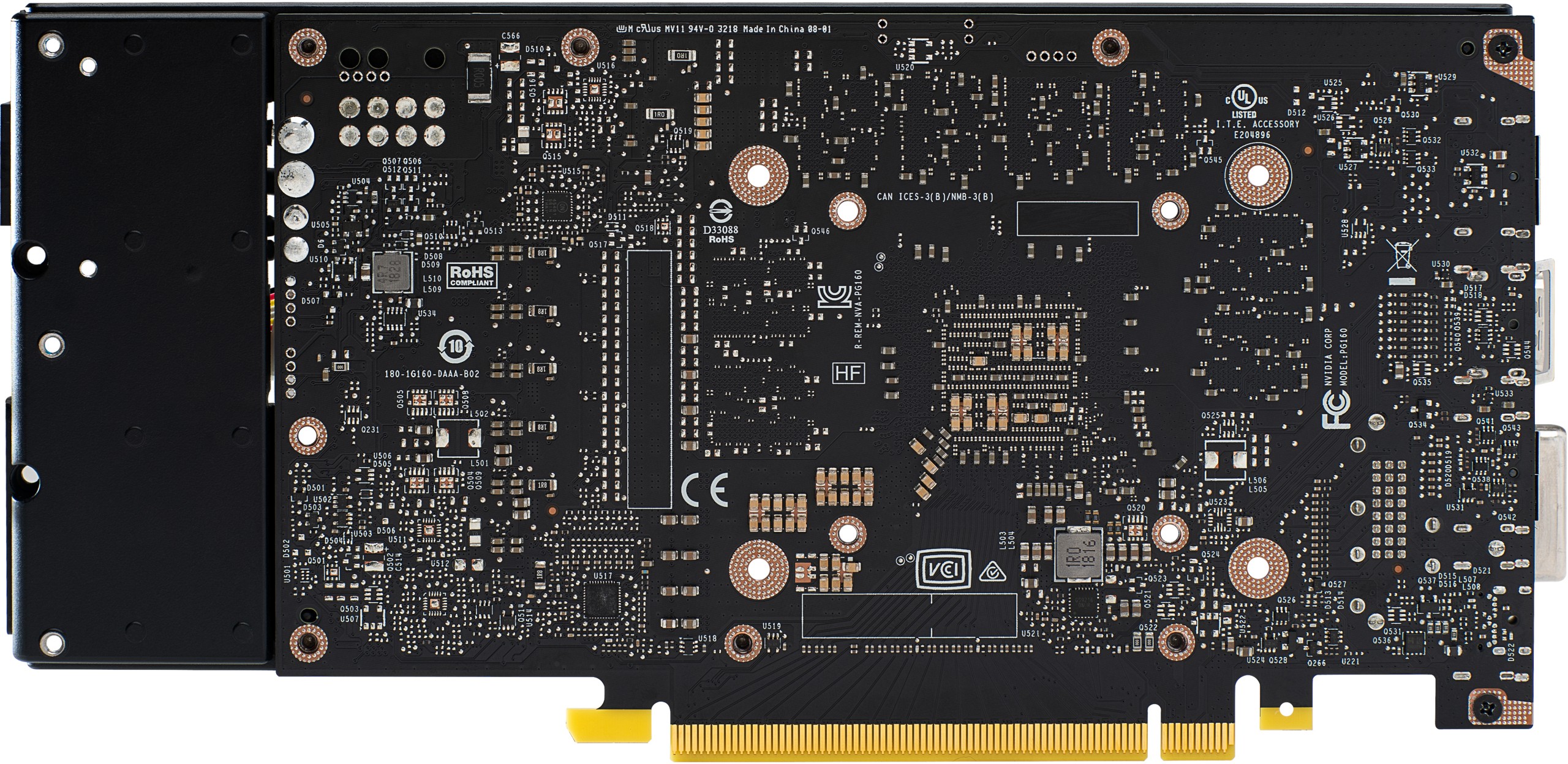
Board layout
I wrote it in the preliminary remark that this time I could only rely on the rendering images and the information I received from friendly colleagues and some partners at the manufacturers. The GeForce RTX 2060 relies on the same 10-layer board with the internal model designation PG160 as the GeForce RTX 2070. Since the TU106-300 is similar to the TU106-400 in the circuit, this is quite possible without any problems.

However, this effort is hardly necessary for the simpler card and also makes the whole thing more expensive, because this card can also be produced significantly more cheaply, if you can rely as a board partner on the new GP161 layout, for which only a significantly cheaper 6- layer board. Here, one calculates with February 2019 for the start of mass production. However, it is unlikely that a particular model with two different boards will be offered.
But whether 10- or 6-layer design, all proprietary designs of the manufacturers must again be based on Nvidia's "Base Design Kit", which is binding for the AIC. And this is exactly where any delay becomes the causal chain until the later start in the retail trade. But back to the reference board.
We see six simple voltage converter phases for GPU power supply, as well as two more for memory. For the GPU, you rely on an uP9512R, which could generate up to 8 phases, but only has to deliver 6. The memory is provided by a small uP1666, which only needs to deliver two phases. Both PWM controllers are from UPI.
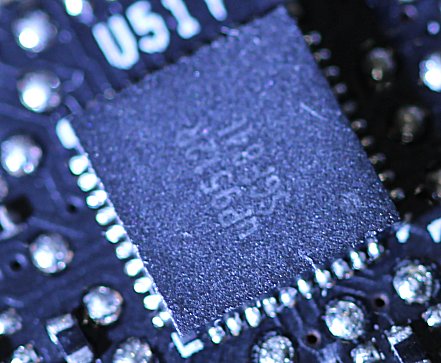
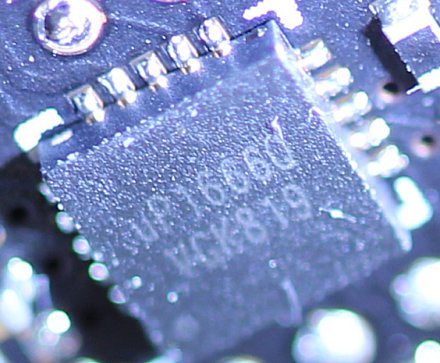
With the NCP 302155 from ON Semiconductor, the nCP 302155 will take over a total of eight (6+2) low-cost dual MOSFETS for the high- and low-side, which also have an integrated driver. The significantly more expensive and better Smart Power Stages of the 2080s cards are dispensed with in favor of costs. However, the monitoring of current flow and temperatures is also eliminated (IMON, TMON).
Thus, the GeForce RTX 2060 differs very clearly from what we wrote in the theory article on the 8-phase voltage supply and the quality of the voltages generated. It's a pity, because the PCB really goes more in the direction of GeForce GTX 1060 in complexity. Interesting, however, is the relatively new uP7561Q, a Two Channel Power Input Management IC for monitoring on the back.

The whole thing is smoothed for the GPU with the usual 220mH coils, with the memory it is even some with 470mH. As always, they are encapsulated and encapsulated ferrite core coils, but from a different manufacturer than usual. The fact that the card has a single BIOS is no secret and I couldn't see any other subtleties in the pictures. Which I would be able to get through with.
The memory is 8GB GDDR6 SGRAM modules (2 channels x 256 Meg x 16 I/O, 2 channels x 512 Meg x 8 I/O) with a bandwidth of 14Gb/s. Since a total of six modules are installed, the memory expansion of 6 GB is also available. The vacancies on the board have been cleverly left exactly where the nasty hotspots usually sit when fully-fitting. Also a solution.
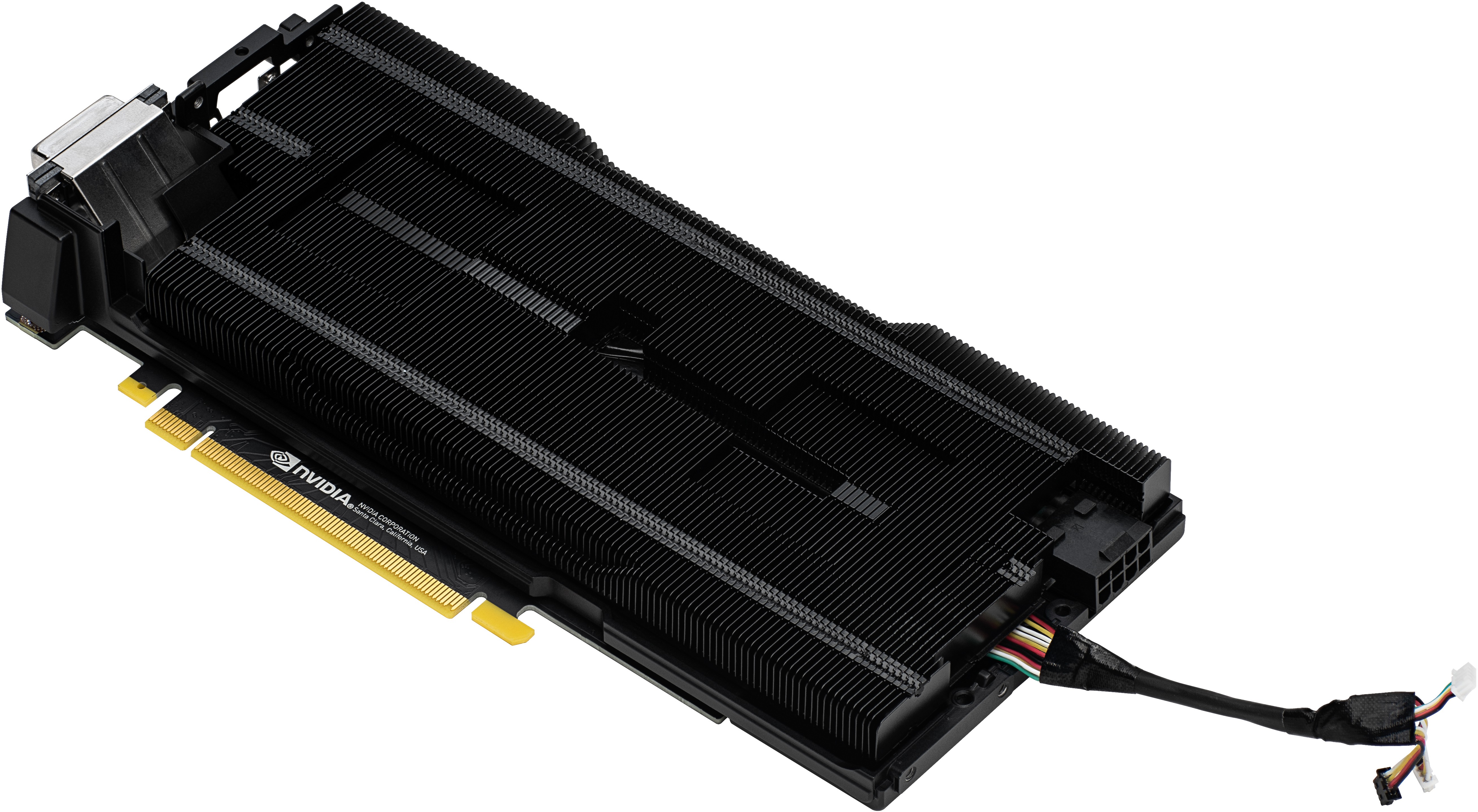
Cooler
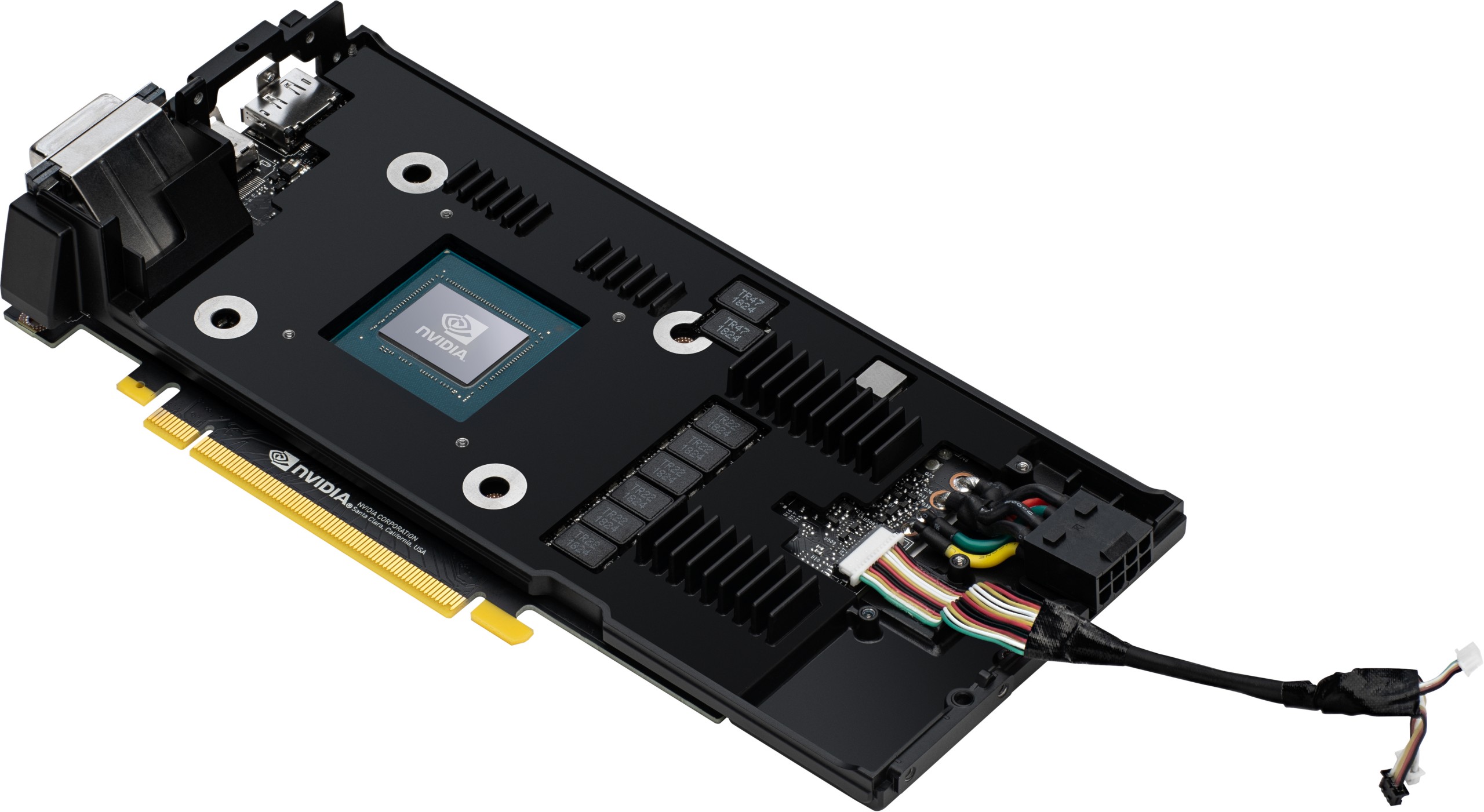
No, you can only completely dismantle the cooler yourself if you carefully heat the glue behind the aperture with the RTX 2060 and tear the construction apart with gentle force at the same time. I'd rather leave that and use the render images from Nvidia. Behind the two fans with an 8.5 cm rotor blade and 13 large blades each is the actual cooling block of the GeForce RTX 2070, whose bottom sits on the "probably largest vapor-chamber ever installed on a graphics card".
We also see very nicely on the next picture that the heatsink only has contact with the GPU and the chamber is fixed there with 4 screws. The rest of the board is covered by the large stabilization and cooling frame, which is designed to cool memory modules and voltage converters and is blown from above, as far as the vapor chamber gives it and does not cover everything.
Since the cooler is the same, but the TBP of the GeForce RTX 2060 is slightly lower than that of the RTX 2070, the cooling performance should be one tick better. But more on that later…
- 1 - Vorstellung, Daten und Testsystem
- 2 - Was kann Turing besser?
- 3 - Mesh- und variables Shading
- 4 - DLSS und Raytracing
- 5 - Tear Down: Platine und Kühler
- 6 - Battlefield V (DXR)
- 7 - AotS: Escalation (DX12)
- 8 - Destiny 2 (DX11)
- 9 - Far Cry 5 (DX11)
- 10 - Forza Motorsport 7 (DX12)
- 11 - GTA V (DX11)
- 12 - Metro Last Light (DX11)
- 13 - Shadow of the Tomb Raider (DX12)
- 14 - Ghost Recon Wildlands (DX11)
- 15 - The Division (DX12)
- 16 - The Witcher 3 (DX11)
- 17 - Wolfenstein 2 (Vulkan)
- 18 - Leistungsaufnahme, Temperaturen und Geräuschentwicklung
- 19 - Zusammenfassung und Fazit






























Kommentieren