So AMD did! Not only that the Threadripper 2 has also been granted the new Zen+ This, as we already find with the Ryzen 2700X and other models of this series, no, one also occupies all four possible places in one of the two models tested today. instead of two, the Ryzen Threadripper 2990 WX elegantly (and almost with a casual gesture from Nonchalance) creates the first 32-core CPU (64 threads) for the inclined consumer outside the server worlds!
Sure, the buyer will still have to settle for quad instead of octa channel due to the fully stocked model, but the whole thing has been almost lossless on the X399 boards, even if you can't access two memory controllers Can. The benchmarks from all possible fields of application that follow will certainly show this impressively.
And so not only has the Ryzen Threadripper 19950X got a worthy 16-core successor with the 2950X, but a monster CPU has arrived on the market for the first time, whose uses and areas want to be thoroughly researched before a possible purchase and also Should. After all, the legitimate question really arises as to who needs such CPUs at all and, if so, what they can actually do in the end.
And if it weren't humiliating enough for the competitor, you cool the whole truck up to the overlong 32-tonne with air! Well, there are of course physical limits here, but I have a total of five different cooling solutions or cooling solutions. methods and later explore in detail who needs what and how much performance at all. But it is possible, that much is certain. You don't even have to hide a chiller under the table.
Threadripper, the Second
The Ryzen Threadripper 2950X and 2990WX, analogous to the Ryzen 2xxx, no longer rely on GlobalFoundries' 14nm LPP node, which can be found on the first-generation Threadripper models, but on GloFo's new 12nm LP process technology. Although the naming conventions for semiconductor nodes have become more of a marketing bubble that is not based on the traditional method of gate length and pitch measurements, new process technologies still provide noticeable Improvements.
GlobalFoundries' new 12nm LP process offers shrinkage in lithography as well as further process improvements. AMD has ported its 14nm design to 12nm, but actually only uses the improvements in process technology to increase the switching speed and thus the performance of the transistors, so that the actual area and the transistor density remain the same. The number of transistors of a Dies is therefore also approx. 4.8 billion and you also use the identical area of 213 mm2 per die compared to the previous models.
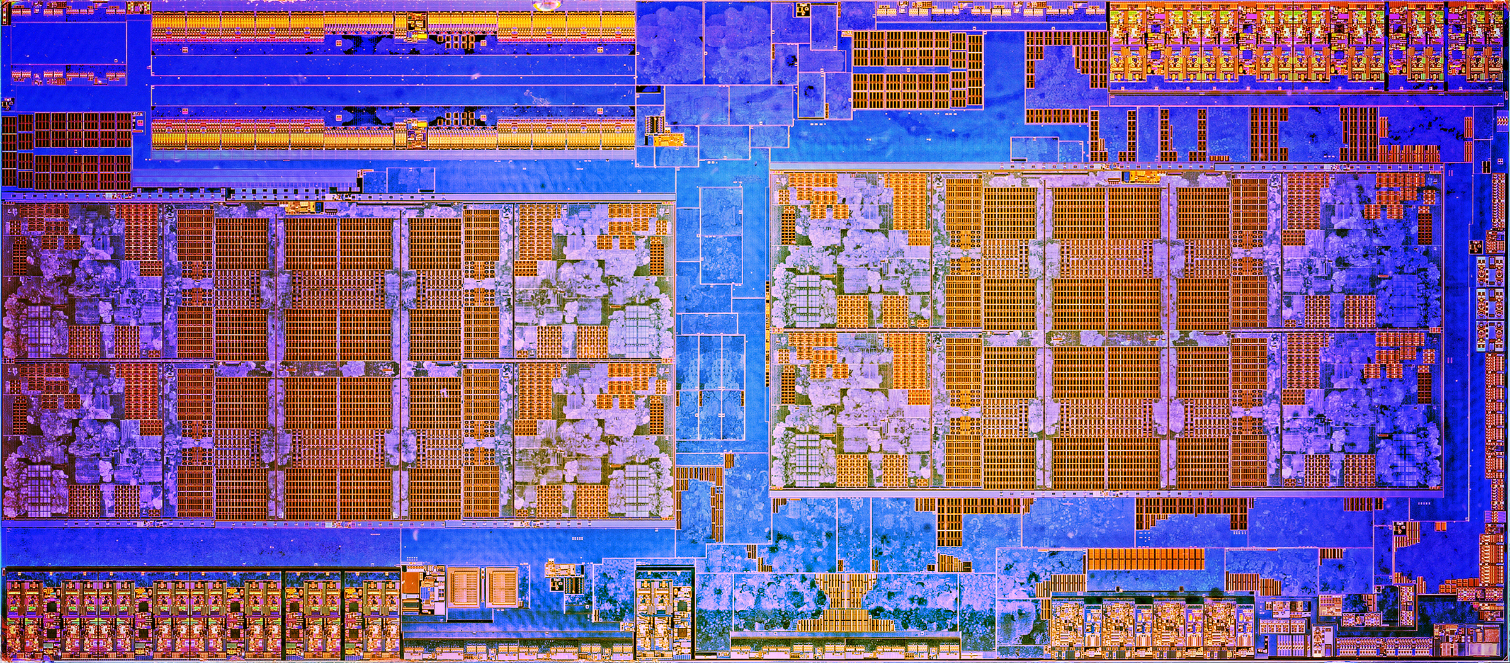
The refined process also guarantees significantly lower leakage currents. These energy savings give AMD room for further improvements, allowing some of the additional power and thermal leeway to be used for Precision Boost 2 and invested in the XFR2 algorithms. AMD also improved the L1, L2, and L3 cache latency we've seen with the Ryzen Threadripper processors, and also reduced memory latency by 11%.
AMD intentionally offers customers the familiar enthusiast features, such as Indium lot between the Die and the IHS to improve the efficiency of heat transfer. The combination of cooler and indium solder stands in stark contrast to Intel's Core i9-79xxX(EE), which use a standard thermal paste between Die and Heatspreader and, due to lack of relevance, are not delivered with a boxed cooling solution ex-factory. How about?
Precision Boost 2 and XFR2
Although AMD's previous generation of Threadripper processors already had Precision Boost, a Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling (DVFS) implementation similar to Intel's Turbo Boost, and eXtended Frequency Range (XFR), which provides an additional frequency increase if your cooling solution offers only enough thermal room for manoeuvre. However, they only offer dual-core or all-core precision boost and XFR clock frequencies.
Many applications (e.g. Games) relieves other threads of less critical tasks, but work with multiple threads without really properly utilising all of them at the same time. these rather light-weight "helper" threads still load the cores enough to trigger the lower full core frequency as a result, which will unnecessarily affect performance on these lighter workloads even though the processor is actually power reserves and thermal leeway to operate within the limits even at higher frequencies.
The new Precision Boost 2 algorithms (which recently debuted on the desktop with Raven Ridge processors) and XFR2 improve performance in multithreaded workloads by increasing the frequency of any number of cores and threads. Precision Boost 2 ends up delivering up to 500 MHz more clock speed on real multicore workloads, while XFR2 delivers an additional boost of 7% if the cooler is strong enough.
These improvements finally extend the benefits of already strong multi-threaded performance to a larger number of concurrent workloads, but only as long as the processor 68°C Tcase (i.e. 95 °C Tctl) or the set limits for current flow underthe Otherwise it will be less. However, we have a very interesting experiment with five different cooling solutions in petto later.
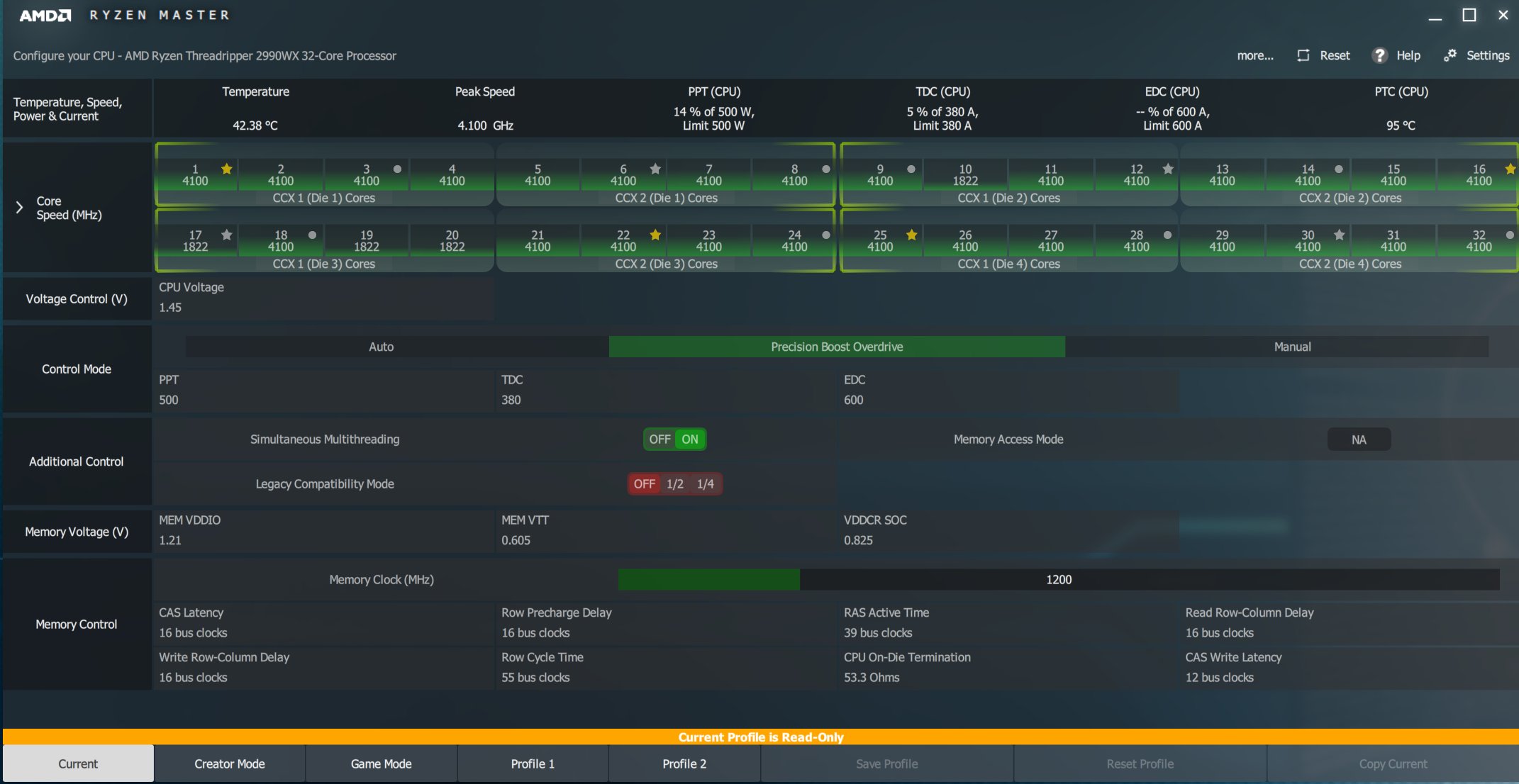
The new Ryzen Threadripper simphers communicate with the motherboard power subsystem to evaluate performance based on existing power supply capabilities. The processor monitors variable package power tracking (PPT) and thermal design current (TDC) to keep the distance from the maximum output power or to the power of the motherboard. The Electrical Design Current (EDC) also defines the maximum possible current from the VRMs under peak/transient conditions.
The control loop then redirects the real-time telemetry data to the Infinity Fabric, which allows the processor to dynamically modulate performance based on heat and performance conditions in real time. AMD provides some of these monitoring features, such as PPT, TDC, and EDC with its updated Ryzen Master 1.4 overclocking software – if the motherboard BIOS supports it.
Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO)
AMD has also updated the Overclocking software Ryzen Master to version 1.4.x for the new Threadripper and added additional functions up to the Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO). The software identifies the fastest cores using a colored star and point ranking and communicates perfectly with the motherboard power delivery subsystem, which offers many new overclocking monitoring functions. The two thread rippers also feature an improved SenseMI suite, as amD's 2000 Ryzen series.
But what is behind PBO? The overdrive framework is currently available in the Ryzen Zen+ CPUs and the X470 and X470 and X470. X399 platforms. Overdrive is now a feature that is available for the first time with the new Ryzen Master tool and the latest BIOS versions. Everything xFR2 and Precision Boost 2 are doing at the moment is also based on overdrive. In the end, you can think of Overdrive as a more aggressive Precision Boost 2.
What overdrive can do more than Precision Boost 3 and XFR 2 is even more stringent monitoring of VRM usage (e.g. Socket Power Capacity and VRM Capacity) on the motherboard to see if there is still enough power to supply. If one is detected, Precision Boost Overdrive can slightly nullify the vCore limiter (allowing higher vCore voltages) on the CPU. This allows the CPU to operate beyond the actual specifications and factory settings. However, this is also outside the scope of the warranty.
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 2990WX, 32C/64T, 3.00-4.20GHz, boxed ohne Kühler (YD299XAZAFWOF)
 | lagernd (1 Stück), Lieferung sofort möglich | 1660,05 €*Stand: 27.07.24 03:12 |
 | Lieferzeit 4-8 Werktage | 2228,00 €*Stand: 26.07.24 22:51 |
On the next page, as a new service specifically for this launch, we have provided both the briefing video stream and the most important slides on AMD's technology and strategies.

































Kommentieren