So far you know me mainly from the forum as a helper with hardware problems. Since similar questions often come up, Andreas (ApolloX) asked me if we could create some tutorials. I’ll start here with an article about the possibilities Windows itself offers for troubleshooting. If you would like to create tutorials as well, please feel free to contact Igor.
Windowstools
I would like to present you a few useful Windows tools that can be used to search for information about error causes. Which tools can help you further, of course, varies depending on the problem. That’s why I just want to give a rough overview of different possibilities. I intentionally put the “Performance Monitor”, the “Event Viewer”, the “Device Manager” and the “Task Manager” at the beginning because these tools are most likely to show where a problem lies. The other tools are only needed if you want to investigate a problem in a specific area in more detail.
Partially, you can solve the problems right away with the tools. Otherwise, the tools provide you with the information you need to successfully search for help on the Internet.
Call tools
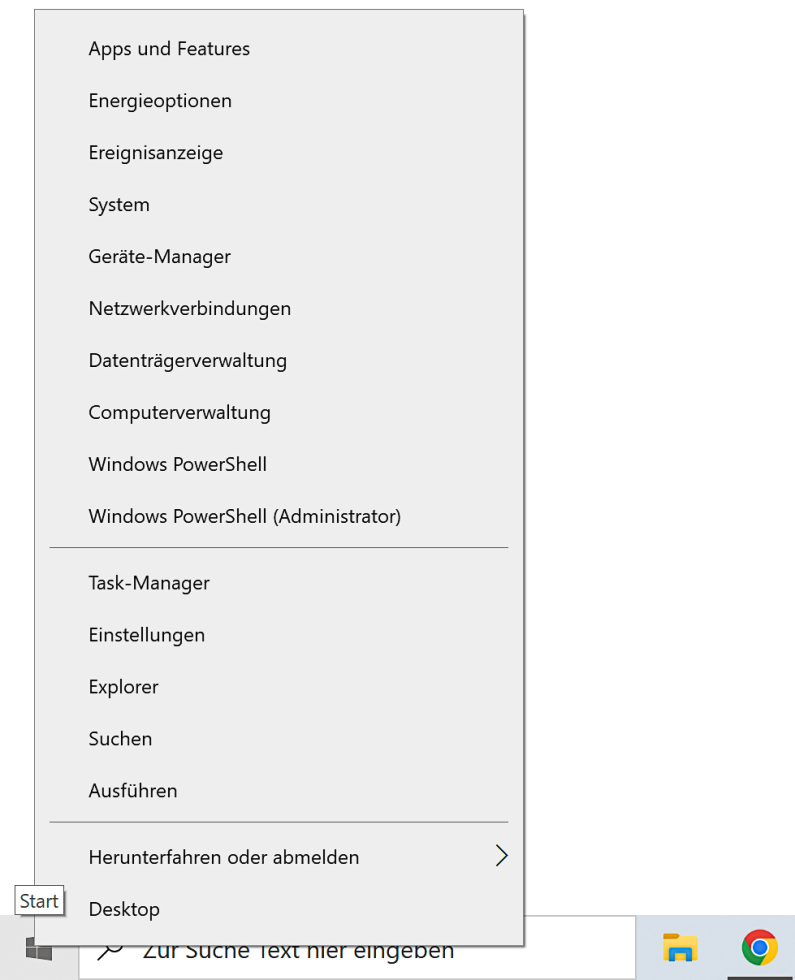
You can start some of the tools in a context menu that opens with a right-click on the Windows icon in the lower left corner.
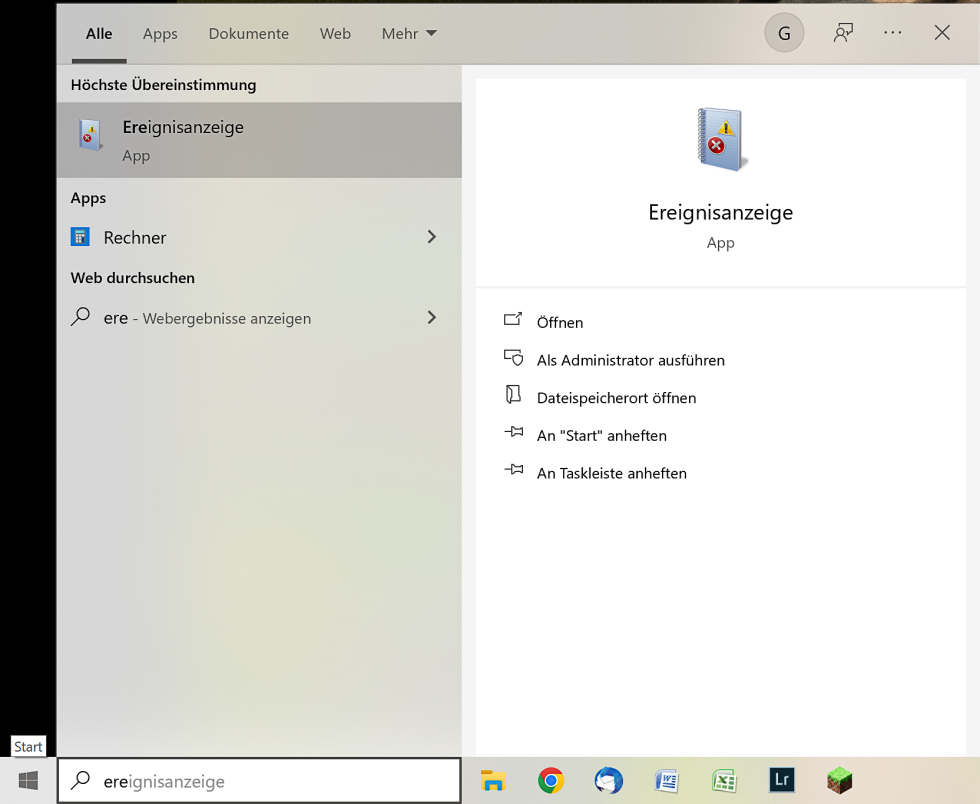
You can quickly find most tools by typing the beginning of the name in the Windows search box.
You can also access the tools from the Control Panel menus. Since these are differently arranged in each Windows version, I do without indications here, in which menu something is to be found. My descriptions and photos show Windows 10. The tools look slightly different in other Windows versions, but offer roughly the same functions.
Take notes
I recommend always writing down what you are setting and testing. By fumbling around carelessly, you can get yourself into additional problems and quickly lose the overview. If you have to send in the PC or a component for repair, it is also good if you can describe exactly which error occurs and what you have already tested.
- 1 - Einleitung, Tools aufrufen über Windows Suchfeld oder Kontextmenü
- 2 - Leistungsüberwachung
- 3 - Ereignisanzeige
- 4 - Gerätemanager, Treiber aktualisieren
- 5 - Taskmanager
- 6 - Aufgabenplanung
- 7 - Datenträgerverwaltung, Festplattenpartitionen überprüfen
- 8 - Behandeln von Kompatibilitätsproblemen alter Programme
- 9 - Energieoptionen, Schnellstart Windows ausschalten
- 10 - Wiederherstellung, abgesicherter Start
- 11 - Systemdateien von Windows überprüfen































49 Antworten
Kommentar
Lade neue Kommentare
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
1
Neuling
1
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
Neuling
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Neuling
Alle Kommentare lesen unter igor´sLAB Community →