Liquid metal (LM)
Liquid metal thermal conductive pastes represent an innovative solution in the field of heat dissipation for high-performance electronics. Due to their unique properties, they offer improved thermal conductivity compared to traditional thermal conductive pastes. These pastes are mainly based on gallium alloys, which are liquid at room temperature and have excellent heat transfer properties. However, the use of liquid metal in thermal pastes presents specific challenges and safety concerns. They are characterized by their exceptionally high thermal conductivity, which is significantly higher than that of conventional thermal pastes. This high conductivity is due to the metallic nature of gallium alloys, which enable direct and efficient heat transfer between CPU/GPU and cooler. Gallium forms alloys with other metals such as indium and tin, which remain liquid at room temperature and enable excellent wetting of the contact surfaces. So much for the theory, but there is of course a but…
Gallium plays a central role in the efficiency of liquid metal thermal conductive pastes due to its low melting temperature and high thermal conductivity. It enables an almost perfect fit to the contact surfaces and minimizes thermal resistance. Despite the advantages of gallium, researchers and developers are still looking for alternatives that offer similar thermal properties but without the associated disadvantages such as corrosion and electrical conductivity. Possible alternatives include advanced ceramic-based pastes and carbon materials such as graphene or carbon nanotubes, which also offer high thermal conductivity but are electrically insulating and do not cause corrosion problems. But I have already described this in detail.
Challenges and safety concerns
Gallium and its alloys can react with certain metals such as aluminum, which can lead to corrosion and damage to radiators and other components. This reaction is particularly problematic for radiators made of aluminum or contact points made of this material. Liquid metal thermal pastes are electrically conductive, which increases the risk of short circuits and damage to electronic components if used incorrectly. Due to their liquid nature, these pastes require careful and precise application to avoid overflow and contamination of neighboring components:
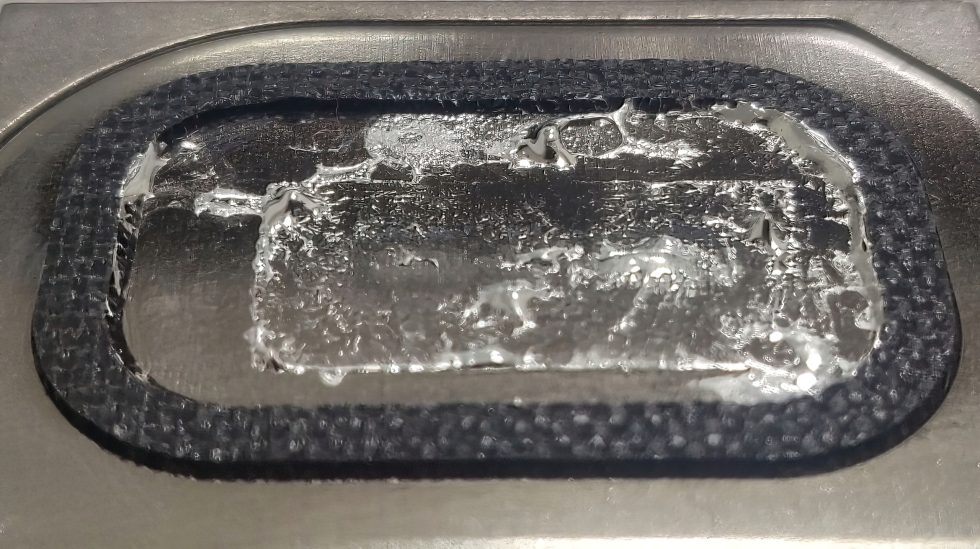

Hardening of radiators
Hardening of radiators refers to permanent damage or changes to the surface caused by chemical reactions between the radiator material and the liquid metal thermal compound. To minimize the risk of hardening, it is recommended to use heat sinks made of materials that do not react with gallium, such as nickel or copper alloys.
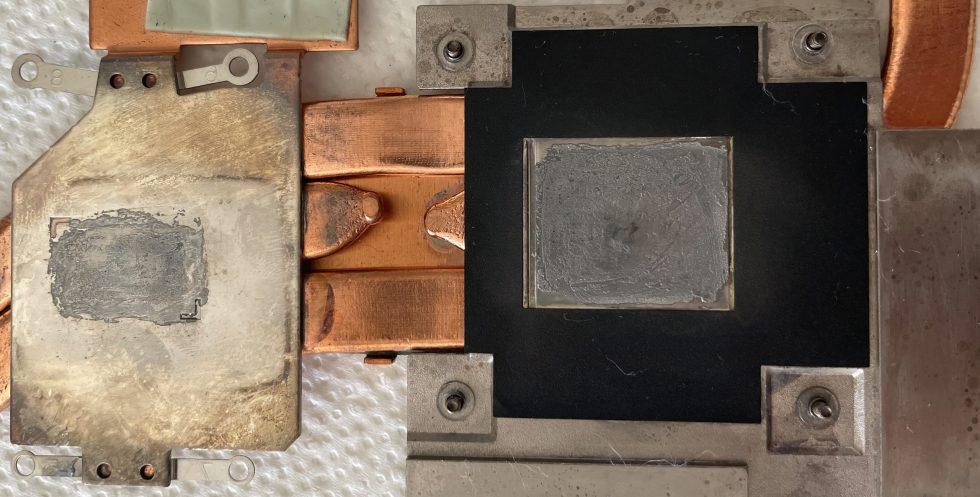
Metal phase change pads (PCM)
Such special pads offer a promising alternative by utilizing the advantages of phase change heat to ensure efficient heat transfer without having to accept the disadvantages of liquid metals. Phase change materials absorb or emit heat during a transition between solid and liquid states, resulting in efficient heat storage or removal. Metal-based PCMs utilize the high thermal conductivity of metals and their alloys to enable fast and effective heat transfer. In the context of cooling, MPCPs convert heat into latent energy instead of just transferring it by conduction.

The manufacture of MPCPs requires precision processes that ensure accurate control of the composition and microstructure of the metal or alloy. This can be achieved by methods such as casting under controlled conditions, sintering of metal powders or electrochemical deposition. The challenge is to develop a material with a suitable melting point, high thermal conductivity and good mechanical stability in its solid and liquid phases.
The MPCPs offer several advantages over conventional TIMs, including liquid metals such as efficient heat transfer, where the use of latent heat provides more efficient heat transfer compared to pure conduction. In the solid state, there is no risk of leakage, which improves handling and long-term stability and reduces the risk of leakage. MPCPs can also expand when heated to fill micro-gaps and re-solidify when cooled, ensuring optimal conformability to surfaces. The ability to switch between solid and liquid states without significant performance degradation increases service life and reliability.
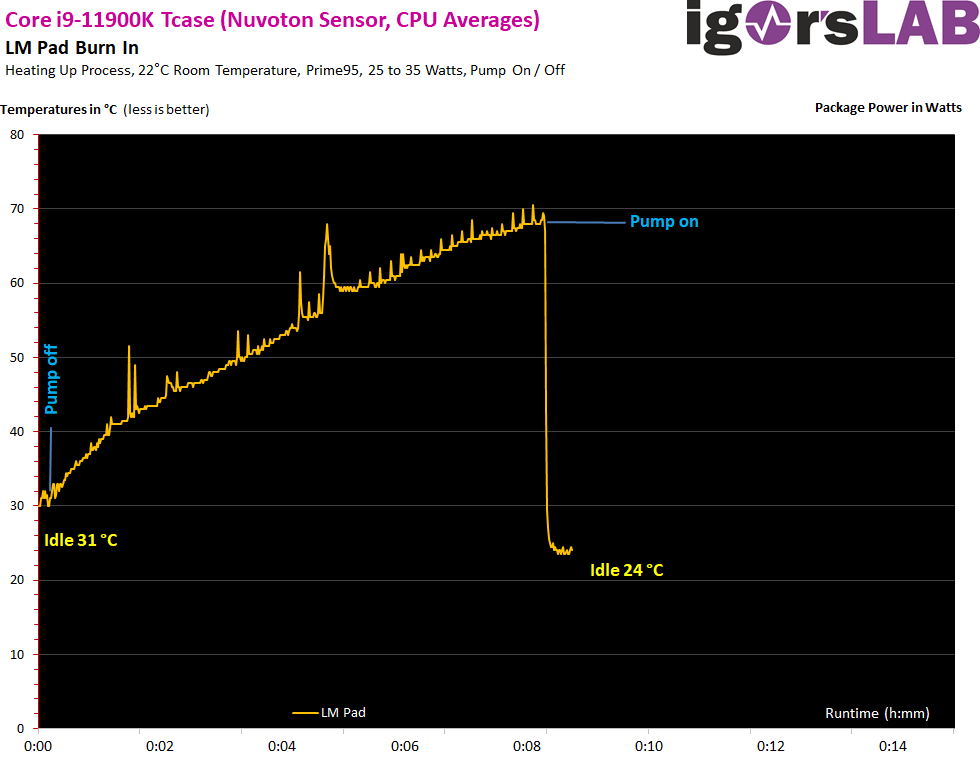
One of my articles from daily practice also shows that handling is not always easy despite all the development progress:
- 1 - The three big P's - introduction to pastes, pads and putty
- 2 - The purpose of thermal pastes
- 3 - The big debate between cheap and expensive
- 4 - The matrix as the basis for all pastes and pads
- 5 - Silicone-based pastes: optimization, durability, decomposition
- 6 - Thermally conductive fillers are important
- 7 - How the degree of grinding influences performance
- 8 - Silicone modification for low temperatures and LN2 overclocking
- 9 - The paste production process and possible hurdles
- 10 - Special case liquid metal (LM)
- 11 - Special case of graphite pads and phase changers
- 12 - Temperature window, expansion behavior, application
- 13 - Ageing and decomposition of pastes and pads
- 14 - Manufacturer vs. bottler, misleading marketing and conclusion

































216 Antworten
Kommentar
Lade neue Kommentare
Veteran
1
Veteran
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
1
Urgestein
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
1
Mitglied
Urgestein
1
Urgestein
1
Veteran
Alle Kommentare lesen unter igor´sLAB Community →