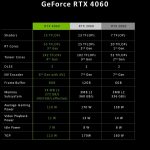
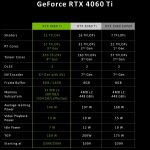
NVIDIA officially unveiled its mid-range RTX 40 graphics card lineup today, which consists of three different models, although it’s not a real launch with benchmarks and unboxing yet. Of particular note here, however, is the RTX 4060 Ti, which will launch in two variants with 8 GB for an MSRP of €439 and with 16 GB of video memory (VRAM) for €549, respectively. Interestingly, this means the mid-range RTX 4060 series will actually offer more memory than the higher-end RTX 4070 series, which only features 12 GB, even though this 16 GB variant is disproportionately expensive and already comes close to the cheapest RTX 4070. But this particular version could indicate that NVIDIA is focused on one hand on offering users more flexibility and capabilities for graphics-intensive tasks like playing demanding video games or working with 3D modeling software, or simply on the other hand just reacting to AMD’s permanent memory stabs.
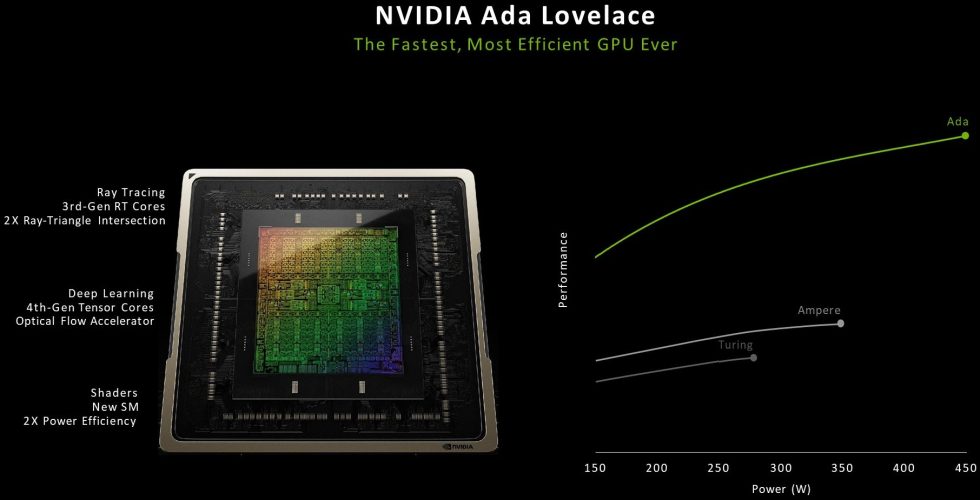
According to the first official data, the RTX 4060 Ti series offers up to 22 teraflops of computational performance with 32 bits of single precision domain (FP32) accuracy. The non-Ti version of the RTX 4060, on the other hand, is said to offer shader performance of around 15 teraflops. NVIDIA compares this data to the RTX 3060 Ti and RTX 3060 models, which deliver performances of 16 and 13 teraflops, respectively. Another important aspect of the RTX 4060 Ti is its power consumption. With a thermal power dissipation (TDP) of 160 W (16 GB variant 165 watts) and an average power consumption of about 140 W while gaming, this graphics card is energy efficient yet powerful.
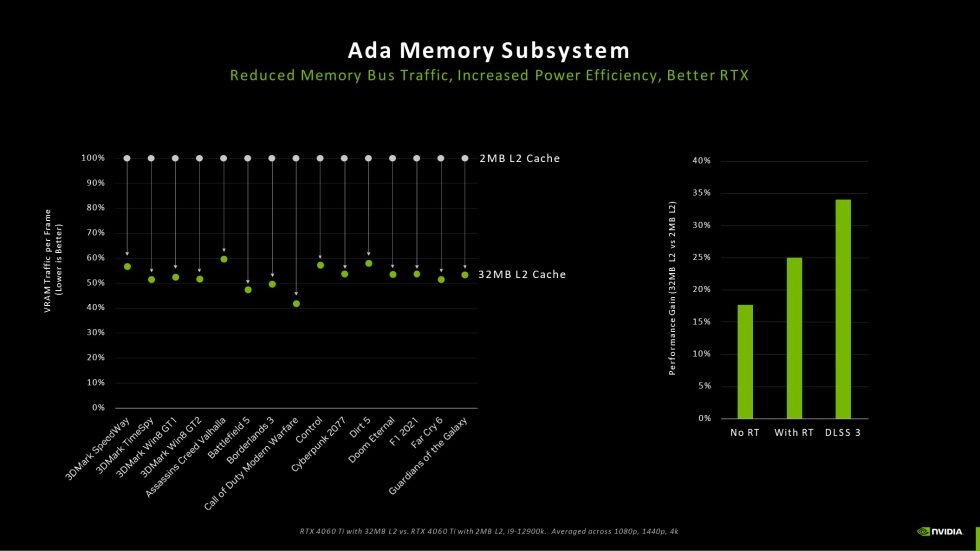
In terms of memory specifications, the RTX 4060 Ti uses 18 Gbps of GDDR6 128-bit memory, which seems surprising at first glance considering the GeForce RTX 3060 Ti’s bandwidths of 488 GB/s or 608 GB/s. However, the significantly expanded L2 cache at Ada Lovelace compared to Amps should be taken into account here: While the GeForce RTX 3060 Ti still has 4 MB of L2 cache, the RTX 4060 Ti will have a 32 MB L2 cache. This reduces the data traffic over the memory bus and thus enables the most efficient combination of performance and energy efficiency for gaming in 1080p resolution.
As you can see in the picture below, all calculations take place in the cores. These must therefore be able to access data quickly and efficiently to meet the demands of modern games. This is where the GPU’s L1 data cache comes into play. Each streaming multiprocessor (SM) has an extremely fast L1 data cache right next to its processing cores, making the L1 the first memory area the GPU looks to for information. However, because of its close proximity to the core, the L1 cache cannot be very large.
If the data needed for processing on the cores cannot be found in the L1 cache, the GPU searches the L2 data cache in the next step. This memory system is located on the GPU chip and is connected to all graphics processing clusters (GPCs), each of which comprises several SMs, via a very fast crossbar system. If the information is found in the L2 cache – a so-called cache hit – then they fetch this data and forward it to the cores. If the information cannot be found in the L2 cache (a so-called cache miss), then the GPU must retrieve the data from the VRAM via the GPU’s memory interface. This results in additional traffic in the memory subsystem and reduces performance and energy efficiency.
Compared to a 128-bit amp GPU, Ada esomit ine’s L2 cache architecture provides a 16x increase in capacity. In addition, the bandwidth of the L2 cache in Ada GPUs has been significantly increased compared to previous GPUs. This enables the fastest possible data transfer between the cores and the L2 cache. Ada’s larger L2 cache results in significantly more cache hits in the L2 area while reducing data traffic over the memory bus.
In contrast, the non-Ti version of the RTX 4060 only relies on chips with 17 Gbps. This means that the non-Ti version has a lower maximum bandwidth of 272 GB/s compared to 288 GB/s for the Ti series. The RTX 4060 will launch with a TDP of 115W, though a typical gaming session should limit power consumption to around 110W. Additionally, all three cards have full support for DLSS3 (Deep Learning Super Sampling), an AI-powered technology that improves image quality while improving performance.
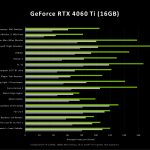
A separate performance score is provided for each RTX 4060 GPU, showing a huge performance boost from DLSS3 (Frame Generation). However, gamers should obviously also look at games without DLSS3 to get a better understanding of where the RTX 4060 models excel compared to the previous generation. Of course, I am not allowed to comment on the exact results yet, but launch day is not far away. Then we’ll all know better (and more accurately).
Furthermore, it should be noted that the graphics card will only have 8 PCIe 4.0 lanes. On older motherboards with PCIe 3.0 slots, this could potentially lead to slight performance losses.NVIDIA does not yet specify the MSRP for the non-Ti version of the RTX 4060 in Euros, but does name an MSRP of $299. This also officially confirms the rumors that this SKU will not hit the market until July. The same release period will also apply to the 16 GB variant of the 4060 Ti. Of course, it remains to be seen what AMD has to offer in return.








































Kommentieren