Tear Down and Board Analysis
Gainward relies on a true own design for this map from the very beginning, but takes over some layout details in the power supply from the reference design. The two ATX power supply connectors are not a special feature. These, like the 12V rail of the motherboard slot, have been provided with a 20A fuse.
Thus, two real rails lead from the sockets to the board. These two rails, as well as the power supply from the motherboard slot, were each provided with a 1-H coil for smoothing possible spikes and each carry a separate shunt for monitoring the current flow.
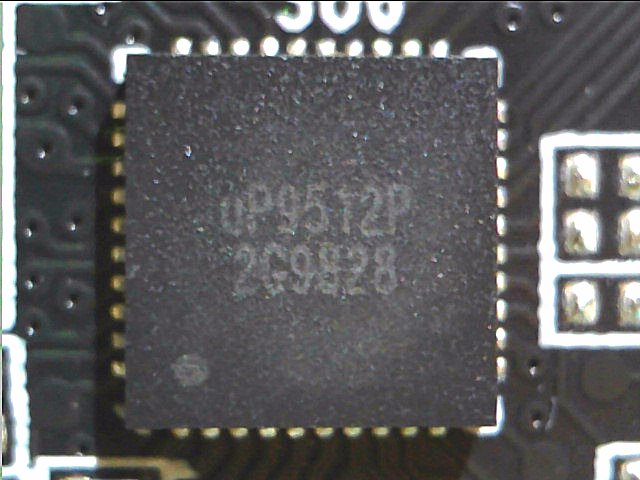
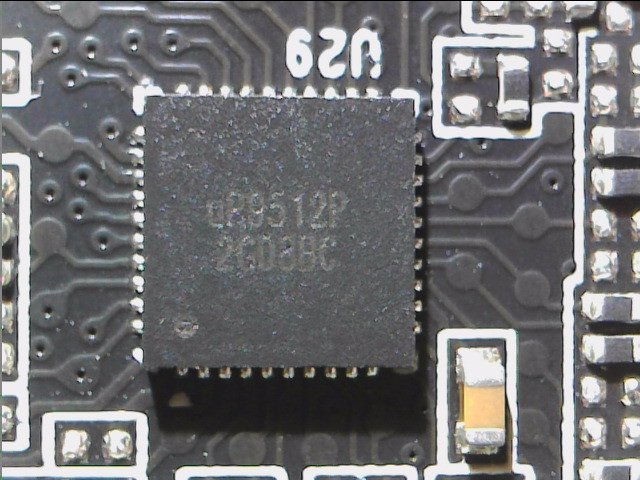
Let's start with the most interesting part! The new uP9512P is used as an 8-phase PWM controller specifically designed to provide high-precision output voltage systems for the latest generation of GPUs. The uP9512P has programmable output voltage and active voltage positioning functions to adjust the output voltage depending on the load current, so that it is optimally positioned for a good load current transition.
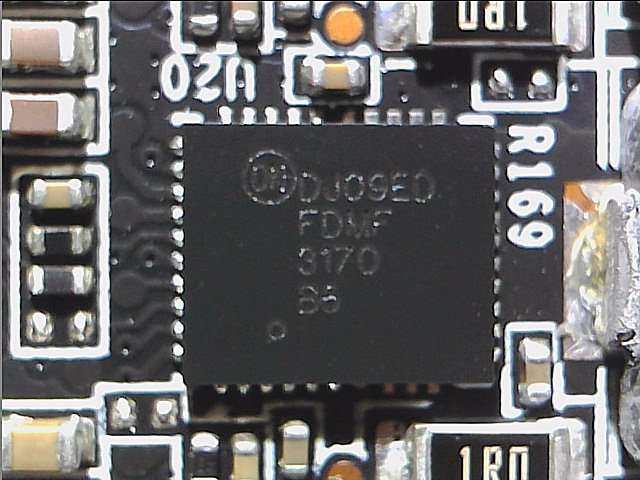
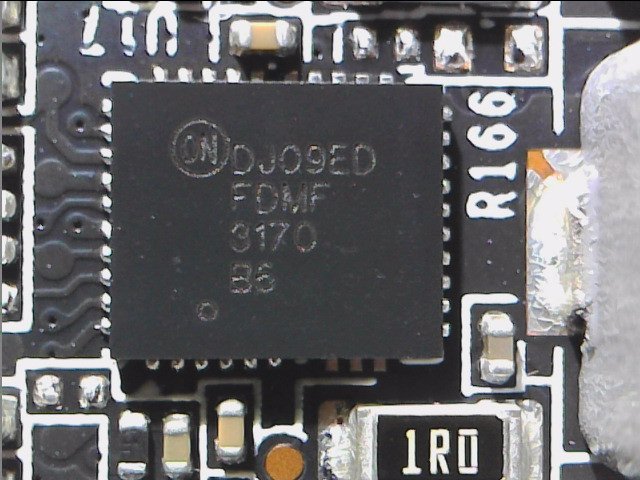
The uP9512 supports NVIDIA Open Voltage Regulator Type 4i+ with PWMVID function. The PWMVID input is buffered and filtered to create a very accurate reference voltage. The output voltage is then precisely controlled on the reference input. The integrated SMBus interface offers enough flexibility to optimize performance and efficiency and also to connect the appropriate software. The controller also supports new Smart Power Stage chips (PLCs). Appropriate PLC then provide very accurate information about e.g. currents (IMON) and temperatures (TMON).
One feature of the uP9512P is the direct parallel connection of several voltage converter circuits without the usual doublers, since due to the necessary direct communication with the PLC no doubler chips can be used. We count a total of 10 voltage converter circuits for the GPU, which would not make sense as single phases. In the simplest of cases, it would only be five real phases, which would also make no sense. However, since you rely on a neat 8-phase design, two phases are double-connected and four more are easy. The two phases for memory are generated by another uP9512P in 2-phase mode.
If you would like to find out more details about this type of power supply and the improvements at Turing, please refer to our Investigative Article "Nvidia GeForce RTX 2080 Ti – Internal Details on Power Supply, Deviating Components and Where the Spikes which is always worth reading. There you will also learn more about the new Smart Power Stages, which replace the traditional, individual VRMs. The following table contains the most important components:
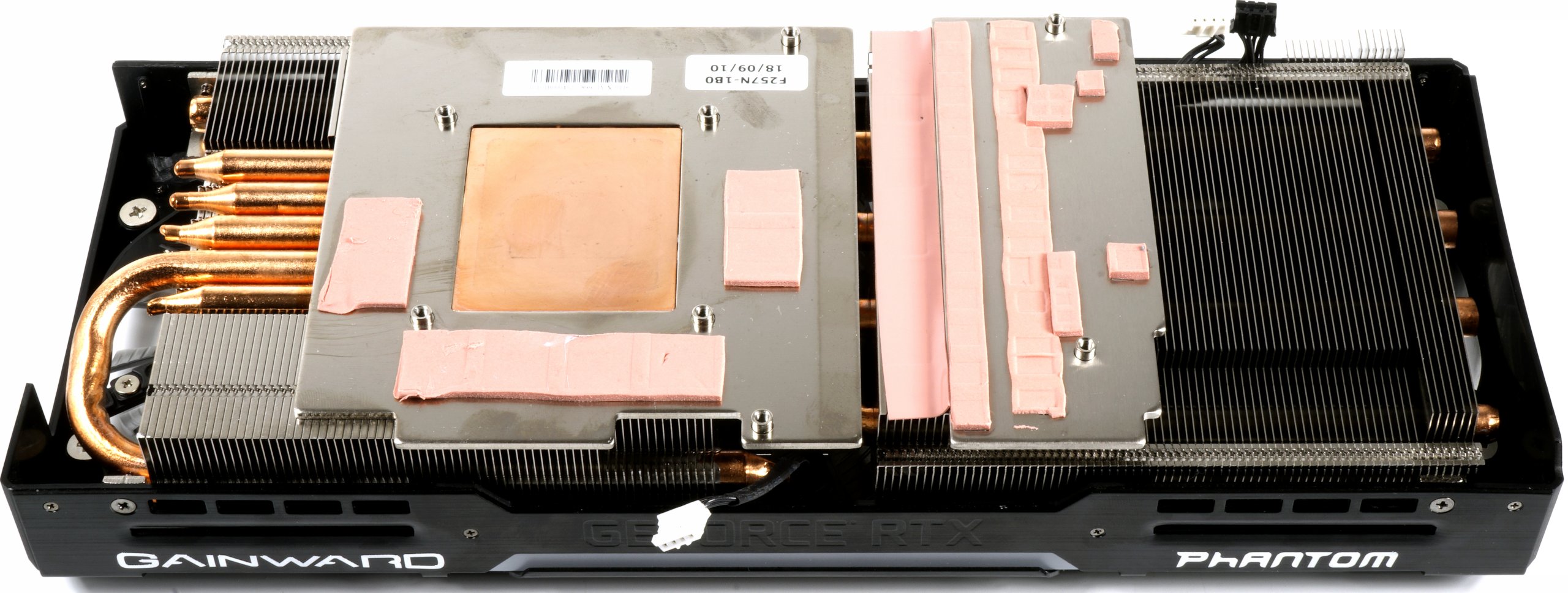
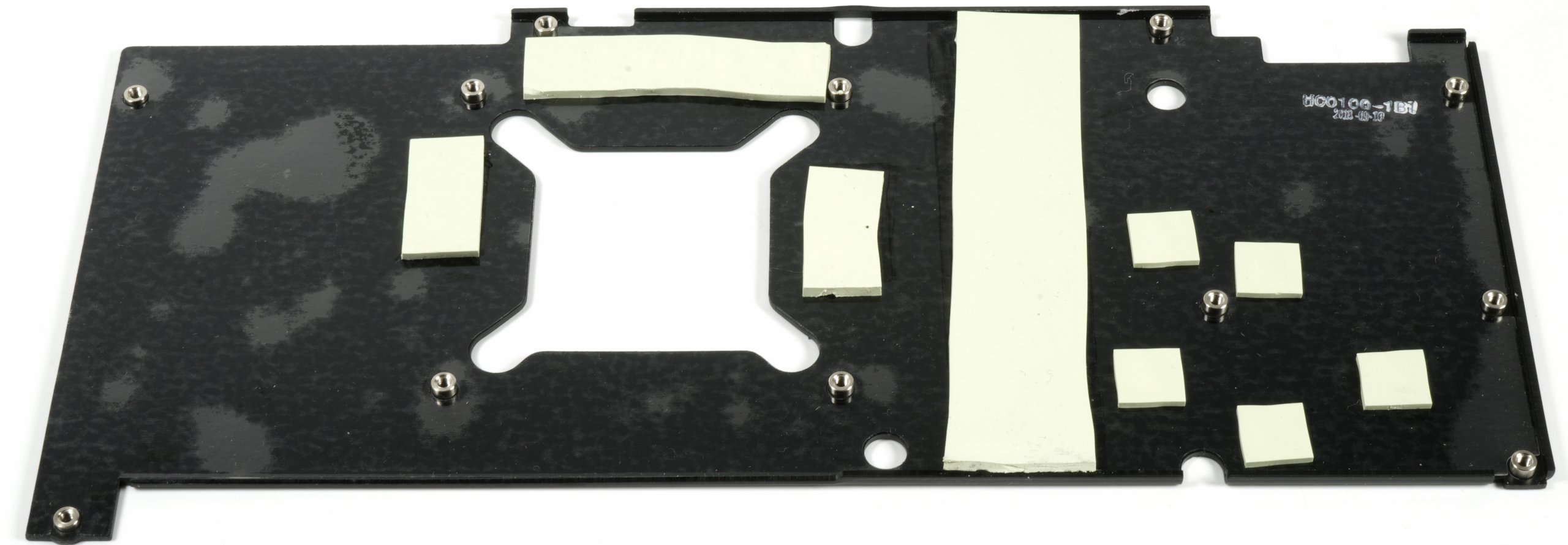
Cooler and backplate in detail
The radiator design does not contain any secrets. Two slat areas sit on a massive heat sink that sits with a copper plate on the GPU, the circumferential metal frame of the radiator construction provides an active cooling of the memory by means of intermediate thermal pads.
A total of 5 thick 8 mm heatpipe then distributes the waste heat to the cooling fins, four of which transport the waste heat along the side to the radiator end, while a heat pipe around the outside of the cooling block above the GPU. Gainward uses a classic fan arrangement with three 8.5cm fans. We can see how well this works.
The brushed backplate made of aluminium indirectly cools the storage via thermal pads, the pads for the VRM would have been saved better, which would certainly have benefited the storage.
| Cooling system at a glance | |
|---|---|
| Type of cooler: | Air |
| Heatsink: | Copper heat sink, GPU and voltage converter for THE GPU |
| Cooling fins: | Aluminum, horizontal alignment related |
| Heatpipes | 5x 8mm copper composite, non-nickel-plated |
| VRM cooling: | 10 GPU VRM via built-in heat sink 2 Memory VRM via built-in heat sink |
| RAM cooling | via heatsink frame |
| Fan: | 3x 8.5 cm fan, 15 rotor blades Only BIOS 2 is semi-passively controlled, otherwise 800 rpm |
| Backplate | Aluminum Cooling function |







































Kommentieren