Intel, one of the world’s largest chip manufacturers, has had to deal with a variety of problems in the server market in recent years. The company, which has traditionally dominated the market for server processors, has lost its supremacy to competitors such as AMD and Qualcomm. Intel’s problems have far-reaching implications for the entire industry and could have an impact on other areas of the company.
Intel also had problems with the production of its processors. The company had difficulty producing its 10-nanometer processors in the required quantities. The delays in manufacturing caused the release of Intel’s latest processor generation to be delayed. This gave AMD and other competitors a head start. Another problem for Intel was the lack of innovation in its processors. Intel’s latest processors had only minor improvements over their predecessors and did not offer the performance and efficiency that customers expected. This gave competitors the opportunity to enter the market with innovative products and features.
To improve its position in the server market, Intel has taken several steps. The company has increased its investments in manufacturing and research and development. Intel has also tried to keep up with its competitors in the multi-core processor market by adding more cores to its own products, and it will take a while for Intel to regain its position in the high-density market. The Intel Sapphire Rapids series has only recently seen wider adoption in data centers and now workstations, after months of delays. However, the company is already planning ahead and will launch its Emerald Rapids series by the end of this year. The series will be based on the same socket, but will feature more cores and support for faster memory.
According to hardware leaker YuuKi-AnS, there will probably be a completely new platform based on the LGE-7529 socle . This platform will be the next generation and will power the Granite eRapid (GNR) and also the Sapphire Forest (SRF-AP) series. Intel Granite eRapid (GNR) is a high-performance computing platform technology designed specifically for use in edge computing applications. Edge computing refers to processing data directly at the source, at the edge of the network, rather than sending it to the central data center infrastructure. The advantage of edge computing is that it reduces latency and cuts down on network bandwidth by not having to send data through the entire network.

Sapphire Forest (SRF-AP) is a platform for cloud-enabled edge computing applications. It is an integrated platform that combines hardware and software components to enable fast and reliable processing of data at the edge. The platform consists of a combination of Xeon processors and FPGAs arranged in a modular architecture. The modular architecture allows users to select only the components they need to meet their specific requirements. In summary, GNR and SRF-AP are both specifically designed for use in edge computing applications. GNR focuses on processing data at the edge with a focus on FPGAs, while SRF-AP provides an integrated platform for cloud-enabled edge computing applications based on a combination of Xeon processors and FPGAs.
Next year, the platform is expected to be launched with DDDR5 memory even faster and more powerful CPUs. The new validation platform “Avenue City RP” for the Xeon series seems to serve this purpose. This could also be the first confirmation that future Xeon CPUs might have a TDP of 500W. The “Avenue City RP” is based on the Birch Stream platform and is a validation reference board for future Xeon series. Measuring 42.4 x 50.8, it features a 20-layer PCB design and offers a total of 24 DDR5 memory slots.
Intel’s next-gen platform will usher in a new era in server processors. The platform is said to support faster DDR5 memory, with speeds of up to 6400 MT/s in a 1SPC/1DPC configuration. This is expected to be a significant improvement over the previous platforms Sapphires Rapid at 4800 MT/s and Emeralds at 5600 MT/s. DDR5 memory not only offers higher speeds, but also higher capacity and better energy efficiency.
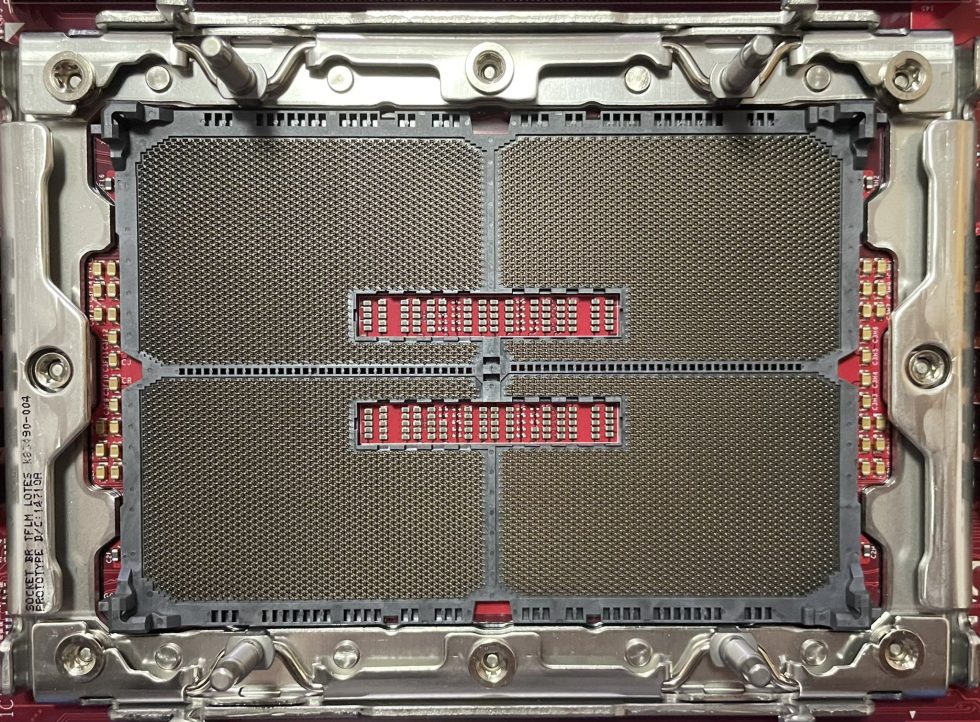
Another interesting feature of the next-gen platform is PCIe lane support. While it is not specified exactly how many PCIe lanes will be available per CPU, it appears that at least 80 lanes per processor will be available. This is the same number as for the Eagle Stream platform. However, this might not be the final specification for this platform.
The next-gen platform will also include two different CPUs, the Granite Rapid and the Sierra Forest. The Granite Rapid will be based exclusively on powerful cores, while the Sierra Forest will be based on the efficient “Atom” architecture. However, both CPUs are supposed to use Intel 3 processor technology. The Granite Rapid is designed for applications that require high computing power, such as in the financial industry or in science. The Sierra Forest, on the other hand, is intended for use in energy-efficient applications, such as telecommunications or the Internet of Things.
Both CPUs are scheduled for market launch in 2024. The exact technical data and specifications are currently not yet known. However, the next-gen platform is expected to offer a significant performance increase over Intel’s current platforms.
Overall, Intel is struggling with a number of problems in the server market. However, there are also some signs that things are improving again. Intel has also announced plans to increase its manufacturing capacity to keep pace with rising demand for processors. It remains to be seen whether these measures will be enough to maintain Intel’s dominance in the server market. However, competition is becoming more intense, and Intel will have to continue its efforts to defend its position in the market.
Source: YuuKi-Ans





























14 Antworten
Kommentar
Lade neue Kommentare
Urgestein
Urgestein
1
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Alle Kommentare lesen unter igor´sLAB Community →