DirectX 12 is a graphics API developed by Microsoft and used in Windows operating systems. An update for DirectX 12 allows the CPU and GPU to access the VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) simultaneously. VRAM is a special type of memory used for processing graphics and videos. Until now, only either the CPU or the GPU could access the VRAM, which could lead to bottlenecks and performance losses. The DirectX 12 update solves this problem by allowing simultaneous access to the VRAM. Simultaneous access allows the CPU and GPU to work more efficiently and improve the computer’s performance. Especially for applications that have high graphics requirements, such as games or 3D modeling, this can lead to a significant improvement in performance. In addition to improved performance, DirectX 12 also offers new features such as improved support for multiple GPUs and better scaling to multi-core processors.
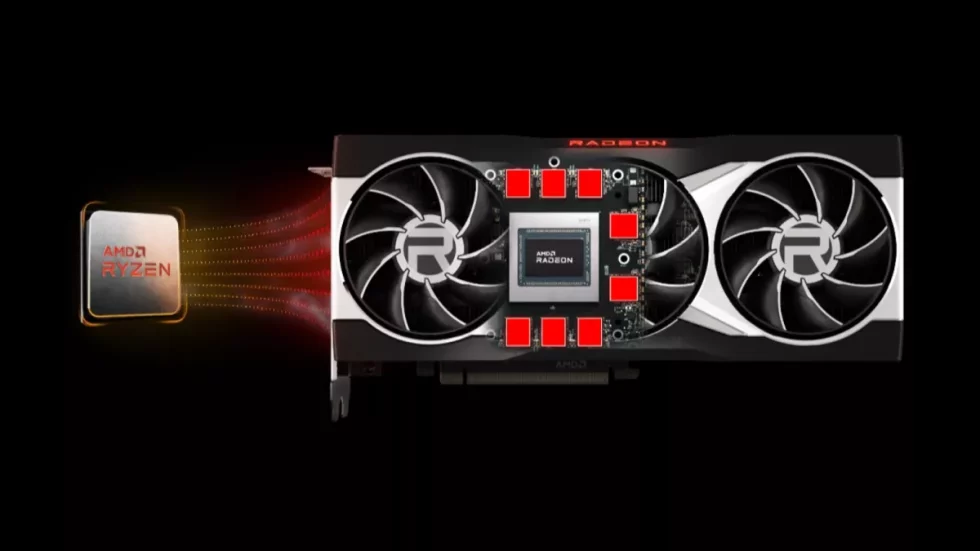

Microsoft has announced a new DirectX12 GPU optimization feature called GPU Upload Heaps that works in conjunction with Resizable-BAR. This function allows the CPU to directly access the GPU memory simultaneously. The use of GPU upload heaps can increase the performance of DirectX12 titles and reduce system RAM usage. Previously, the CPU had to copy data to the GPU, which took time and resources. With GPU Upload Heaps, this is no longer necessary, as the new feature allows direct access to GPU memory. This leads to a higher performance of DirectX12 titles and reduces the load on the system RAM. The new feature is now available in the Agility SDK. The Agility SDK is a software development kit from Microsoft that helps developers create applications for Windows platforms. Developers can now take advantage of GPU upload heaps and optimize their applications for DirectX12 titles.
Since graphics cards and CPUs perform different functions, they often need to exchange information with each other. The graphics card specializes in rendering graphics and processing video content, while the CPU is responsible for general tasks such as controlling operating systems and processing data. If the size of the data that needs to be exchanged between them increases, this can cause the system to slow down. In this context, there is a feature whose exact effects are not yet known, but it is suspected that it could significantly improve performance. If this feature is used, the CPU might be able to transfer data more efficiently between itself and the graphics card, resulting in faster and smoother graphics and video. As the size of the data exchanged between the two components increases each year, this feature could be particularly useful in meeting future technology needs. However, it remains to be seen how effective this feature will actually be and what impact it will have on system performance. Still, there is hope that it will help drive the development of technologies and improve the performance of computer systems.
This feature, makes it possible to noticeably reduce the RAM and CPU usage of a game by reducing data transfers. This is done by no longer forcing the CPU to hold copies of the data in both system RAM and GPU VRAM in order to interact with it. This results in the CPU having to do less work, which has a positive effect on the system’s performance. Another advantage of this feature is that GPU video memory is very fast these days. Therefore, no latency should occur when data is stored only on the GPU. High-end GPUs with high-speed video memory will probably even improve the latency compared to CPU access times. This means that the game can respond faster to requests and perform better overall. Overall, the described feature is a useful way to improve a game’s performance by reducing CPU and RAM usage and optimizing data transfer between CPU and GPU. This can lead to a smoother gaming experience and improve playability.
For gamers, compatibility with Resizable Bar or Smart Access Memory on both the CPU and GPU is a crucial requirement. These technologies allow the computer to directly manage the graphics memory and increase the upload performance on the graphics card. Resizable-Bar is a feature that allows Windows to directly access the VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) of the graphics card and use it more efficiently. This technology allows games and applications to achieve faster load times and better performance. With Resizable-Bar, graphics upload heaps can be used to speed up moving data between the CPU and the GPU. Since the CPU can address the graphics memory directly, the system becomes faster and more efficient overall. This is especially important for gamers, as it allows them to play their games with higher settings and smoother frame rates. Smart Access Memory is a similar technology developed by AMD and specifically designed for use with their own CPUs and GPUs. It allows the CPU to access the entire VRAM of the graphics card and use it more efficiently. This improves performance and allows games to load faster and run at higher settings.
For developers, the feature is already supported by Nvidia, Intel and AMD drivers. For example, it is already included in the latest Game Ready and Studio drivers from Nvidia (version 531.41 or newer) and Intel A-Series/Xe GPUs (with driver 31.0.101.4255 or newer). For AMD GPUs, developers must contact their AMD Alliance Manager to obtain a supported driver. The feature was just released by Microsoft, so it is not expected to be implemented in games anytime soon. Instead, developers will need time to figure out if it offers a sufficient performance advantage to be worthwhile.
Source: TomsHardware






























25 Antworten
Kommentar
Lade neue Kommentare
Veteran
Mitglied
Urgestein
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Neuling
Urgestein
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
Mitglied
Urgestein
Urgestein
Urgestein
Alle Kommentare lesen unter igor´sLAB Community →